What is Hyphema?
Hyphema, also known as blood in the eye, is a condition where blood accumulates in the front chamber of the eye, between the cornea and the iris. The blood may cover most or all of the iris and the pupil, blocking vision partially or completely.
Symptoms of Hyphema
Hyphema can be present with a variety of symptoms depending on the extent and cause of the bleeding. Some people may have no symptoms or only mild discomfort, while others may have severe pain and vision loss.
Some common symptoms include:
- Sensitivity to light
- Pain
- Blurry or blocked vision
- A visible pool of blood in the front of the eye.
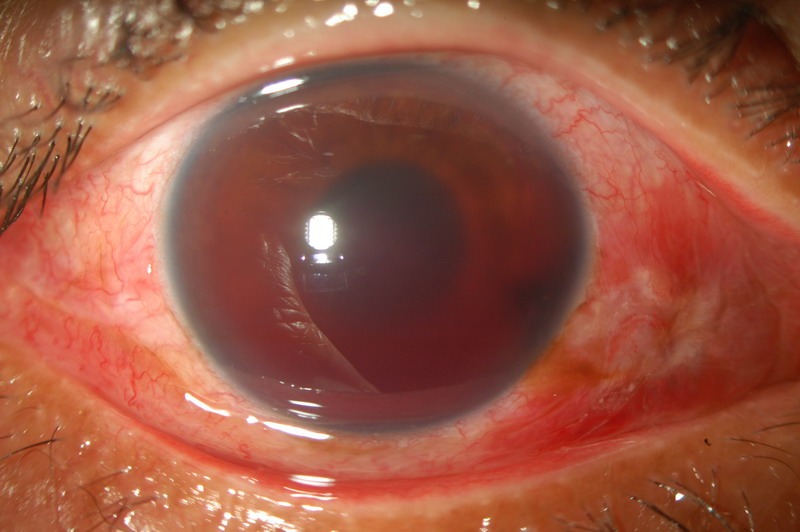
However, it’s important to note that the blood may not be visible if the hyphema is small or located in the back of the eye. If you experience any unusual symptoms or changes in vision, it’s important to seek medical attention promptly.
Diagnosis of Hyphema
To diagnose a hyphema, the doctor will typically begin by taking a complete medical history to identify any recent eye trauma or underlying medical conditions that could contribute to the bleeding. A physical exam of the eye area will then be performed. The doctor may also use one or more of the following methods:
- Comprehensive eye exam: This test assesses your ability to see and identify any visual abnormalities.
- Eye pressure check: This measures the pressure inside the eye using a device called a tonometer.
- Slit lamp examination: This involves using a special microscope to examine the inside of the eye and identify any signs of bleeding or other abnormalities.
- CT scan: If there was trauma to the eye, a CT scan may be done to check for fractures in the orbital socket surrounding the eye.
Depending on the severity and cause of the hyphema, further tests or imaging studies may be needed to assess any potential complications or risks to vision.
Causes of Hyphema
Hyphema, or bleeding in the front chamber of the eye, can be caused by a variety of factors.
Some common causes include:
- Trauma: The most common cause of hyphema is trauma to the eye, which can occur due to accidents, sports injuries, or other physical impacts on the eye.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as sickle cell anaemia, haemophilia, high blood pressure, or diabetes, can increase the risk of bleeding in the eye.
- Eye surgery: Hyphema can also occur after certain types of eye surgery, such as Cataract surgery or Glaucoma surgery.
- Use of blood-thinning medications: Certain medications, such as aspirin, warfarin, and other blood-thinning drugs, can increase the risk of bleeding in the eye.
- Eye infection caused by the herpes virus.
Treatments of Hyphema
Depending on the cause and severity of the bleeding, treatment may be needed to prevent complications and protect your vision. In general, treatment aims to reduce inflammation, prevent further bleeding, and protect the eye from further damage. Some common treatments include:
- Rest and eye protection: Patients with hyphema are often advised to rest and avoid any strenuous activity that may increase pressure in the eye. They may also be given an eye shield or patch to protect the eye and prevent further injury. It is advised to keep the head elevated when sleeping.
- Eye drops: Eye drops may be prescribed to reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and prevent infection. These may include corticosteroids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or antibiotic eye drops.
- Medications: Depending on the underlying cause of the hyphema, additional medications may be needed.
- Surgery: In severe cases of hyphema, surgery may be needed to remove the blood and prevent complications such as glaucoma or permanent vision loss. This is typically reserved for cases where the bleeding is significant or if there is a risk of other complications.
- Monitoring: Patients with hyphema will need to be monitored regularly to check eye pressure.
Complications in Hyphema
A serious eye injury can raise your risk of Glaucoma. Other complications of a hyphema include:
- Damage to your optic nerve
- A stained cornea
- Permanent vision loss
It’s important to seek prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms of hyphema or have concerns about your eye health. With appropriate diagnosis and treatment, most cases of hyphema can be successfully managed, and the risk of complications can be minimized.








