What is Chalazion?
Read this article to know more about Symptoms, Treatments, Prevention and Causes of Chalazion. A chalazion, also known as a meibomian cyst, is a non-cancerous lump or swelling in the eyelid that results from the blockage of a meibomian gland. Meibomian glands are tiny glands located in the eyelid that produce an oily substance called meibum, which helps to lubricate and protect the eye.
When a meibomian gland becomes blocked, the meibum cannot be released, causing a buildup of oil and inflammation in the gland. This can lead to the formation of a small, painless bump on the eyelid, known as a chalazion. Chalazia can occur on both the upper and lower eyelids and can be single or multiple.
Chalazia are usually harmless and disappear on their own within a few weeks to a few months. However, in some cases, they can grow larger and cause discomfort or affect vision. If a chalazion becomes painful, red, or infected, it is important to seek medical attention to prevent further complications.
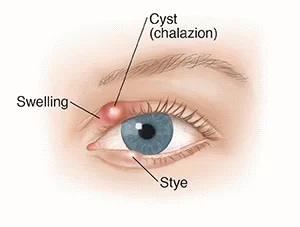
Symptoms of Chalazion
The most common symptom of a chalazion is a painless lump or swelling on the eyelid. Other symptoms may include:
- Tenderness or sensitivity of the affected eyelid.
- Redness or swelling of the eyelid.
- Blurred vision if the chalazion is large enough to press against the eyeball.
- Irritated or watery eyes.
- A feeling of pressure or fullness in the eyelid.
Chalazia usually develop slowly over time and may grow in size before eventually resolving on their own. They typically do not cause significant pain or discomfort, and most people can continue their daily activities without interruption. However, if a chalazion is causing significant discomfort, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the best course of treatment.
Risk Factors and Causes of Chalazion
A chalazion is caused by the blockage of a meibomian gland, which can be due to several factors, including:
- Excess oil production: When the meibomian glands produce an excess of oil, the oil can accumulate and clog the gland, leading to the formation of a chalazion.
- Blepharitis: This is a common condition that causes inflammation of the eyelids and can lead to the development of chalazion.
- Poor eyelid hygiene: Failure to keep the eyelids clean can increase the risk of developing chalazia, as the buildup of bacteria and debris can clog the meibomian glands.
- Certain medical conditions: Some medical conditions, such as rosacea, can cause inflammation of the eyelids and increase the risk of chalazion.
Treatment of Chalazion
There are a few treatment options for chalazia, including home care and medical treatment.
Home care:
- Warm compresses: Apply a warm compress to the affected eyelid for 10-15 minutes, 4-6 times a day. This can help to soften the oil gland and promote drainage.
- Massage: Gently massage the affected area to encourage drainage.
- Good hygiene: Keep the area clean to avoid further irritation or infection.
Medical treatment:
- Antibiotics: If the chalazion is caused by an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection.
- Steroid injections: If the chalazion is large and not responding to other treatments, a steroid injection may be given to reduce inflammation and promote drainage.
- Incision and drainage: In some cases, the chalazion may need to be surgically removed through a small incision.
Prevention of Chalazion
There are several steps you can take to help prevent chalazion:
- Practice good eyelid hygiene: Regularly clean your eyelids and eyelashes with a gentle cleanser to prevent the buildup of oils and bacteria that can clog your glands.
- Avoid rubbing your eyes: Rubbing your eyes can irritate the eyelids and increase the risk of developing chalazia.
- Manage underlying conditions: If you have an underlying condition such as blepharitis, rosacea, or seborrheic dermatitis, work with your healthcare provider to manage the condition and reduce your risk of developing chalazia.
- Avoid using expired makeup or sharing makeup: Expired makeup can harbor bacteria that can cause infections and inflammation, leading to chalazia. Also, sharing makeup can increase the risk of infection.
- Use warm compresses: Applying a warm compress to your eyelids can help open the blocked glands and prevent the formation of chalazion.
In conclusion, a chalazion is a small, non-infectious lump that forms on the eyelid due to a blocked oil gland. While they can be uncomfortable and painful, there are several treatment options available. It is important to seek medical attention if you are unsure about the type of eye condition you have or if your symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment.








