India is known as the diabetes capital of the world, and Bangalore has the highest prevalence rate of diabetes in entire India, so many diabetic patients come here for their treatment. Nowadays, diabetes is prevalent in younger age groups as well.
What is Diabetes
 ?
?
Diabetes is a disease in which the human body’s capacity to generate or react to insulin is affected, resulting in atypical carbohydrates and increased glucose ranges within the blood. It is a silent disorder that impacts many body organs, including the eye.

What is Diabetic Retinopathy?
Diabetic retinopathy is a disease that affects the retina (the veil of the eye where the image is formed) of a person having diabetes. It is caused by damage to the fine tubules that carry blood to the retina. If not taken proper care and treatment, it can lead to total blindness.
“Diabetic Retinopathy can cause total blindness if it is not treated and preventive measures are not taken on time”.
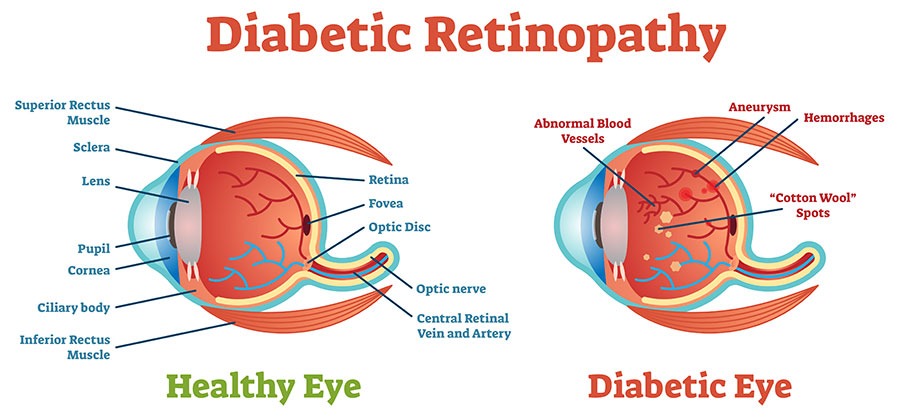
More than 40% of diabetic patients suffer from diabetic retinopathy. It is one of the most common causes of blindness in the world. Although only a person with diabetes can have this disease as diabetes progresses, the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy increases. Diabetic patients with coexisting high cholesterol and high blood pressure are at increased risk of blindness.
Watch about Blindness Due To Diabetic Retinopathy on Shekar Eye Hospital YouTube Channel.
How does diabetic retinopathy occur?
Diabetic retinopathy occurs due to uncontrolled and high blood sugar levels for a long time. Excessive blood sugar levels damage the blood vessels which carry the blood to the retina. Damaged blood vessels cause fluid leakage within the retina’s layers, affecting vision.
How does Diabetic Retinopathy damage vision?
Blood vessels inside the eye get damaged due to increased sugar levels in the blood, causing inflammation in the retina and disrupting the supply of oxygen – a nutrient needed to keep the retina healthy. Blind spots are formed in the eye due to inflammation, bleeding and fluid collection, which can also cause a sudden drop in vision.
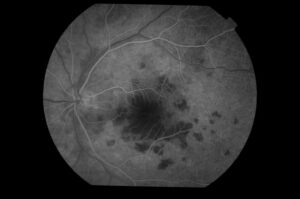
Types of Diabetic Retinopathy:
Non – Proliferative retinopathy: –
It is the initial stage of diabetic retinopathy, also known as “Background Retinopathy”. This is because new blood vessels do not form in the initial phase of the disease. However, there is a risk of leaking fluid from the damaged blood vessels in this stage.
Proliferative retinopathy:
It is also called advanced retinopathy. It is the stage of retinopathy, in which new blood vessels start growing within the retina. These vessels are usually abnormal and develop in the center part of the eye.
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy
- Disturbance in vision due to swelling of the macula (center of the retina).
- Shapes like a spider web, mosquitoes are seen (called floaters).
- Excessive bleeding can lead to sudden and profound loss of vision.
When does the risk of getting diabetic retinopathy increase?
The following situations can increase the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy:
- The longer the duration of diabetes, the more the risk of diabetic retinopathy.
- Uncontrolled blood sugar levels

- Co-existing High BP & cholesterol

- Pregnancy
- Chewing tobacco/smoking/alcoholism
- Old age

How to test Diabetic Retinopathy?
The most recommended way to diagnose diabetic retinopathy is a comprehensive dilated eye examination. First, a drop of a particular medicine is put in the eyes to dilate the eyes. As a result, the eye pupil enlarges, and the inside of the eye is seen well.
Although, for some time, blurred vision is caused by instilling this drug, the blurring effect usually lasts a few hours.
Doctors may do two more types of tests. They are:
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT):
The doctor may suggest you have an OCT test. This type of imaging test takes cross-sectional pictures of the retina from different directions, by which the thickness of the retina is detected. For example, if there has been a leak of blood or fluid in the retinal tissue, it becomes detectable with the help of this test. Later OCT testing can also determine if the treatment is working well.
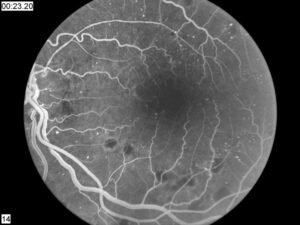
Fluorescein Angiography:
With the eye wide open, the doctor takes pictures of the inside of your eye. After that, with the help of injection, a particular type of dye is injected into a vein in the arm, and again, pictures of the eye are taken.
This specific dye circulates in the eye’s blood vessels and demarcates the retinal blood vessels in the photographs taken. Therefore any blockage or damage in the blood vessels becomes visible.
How diabetic retinopathy can be prevented?
The risk of diabetic retinopathy can be decreased by taking certain precautions, such as:
- Regular dilated eye examination once a year
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet with reduced salt, fat, and sweeteners.
- Regularly check blood sugar, blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Talk to your doctor about a glycosylated haemoglobin test. The glycosylated haemoglobin test shows the average of your blood sugar level over the past few months. Most people target a value of less than 7% in the HbA1c.
- Regularly urine test for ketone levels
- The strict control of diabetes with insulin, medicines and exercise.
- Giving up alcohol, smoking and tobacco use.
What is the treatment for diabetic retinopathy?
The treatment of diabetic retinopathy is done by considering the stage in which it is. The main goal of any treatment for diabetic retinopathy is to prevent or reduce the complications of the disease.
To control diabetes, the patient has to seek the help of a doctor. If the blood sugar levels are under control, it helps in reducing diabetic retinopathy progression to a great extent.
- Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) drugs:
These medicines can reduce fluid buildup in the retina. These drugs also stop the development of abnormal new retinal blood vessels. The eye is numbed, and a thin needle injects this drug into the eye. This injection improves vision by keeping the retina dry.
- Laser Treatment:
In cases of proliferative diabetic retinopathy, laser treatment can be done to treat the abnormally developed blood vessels in the retina. Laser treatment is very effective in treating blockage or leaking of blood vessels. But how successful this procedure is depends on how long the blood vessels have been clogged or leaking.
- Eye surgery:
There is no complete cure for diabetic retinopathy with the help of surgery. Retinal surgeries help restore the structure, but the recovery of the function of the retina depends on the extent and duration of the damage. Diabetes is a chronic disease, and despite medical, surgical or laser treatment, it can lead to retinal damage and reduce vision.
Diabetic Retinopathy Risks & Complications:
Some of the possible complications related to diabetic retinopathy are as follows:

As the new blood vessels form in the retina, fluid flow inside the eye is disturbed. Due to the blockage of fluid flow, the pressure inside the eye increases, which increases the risk of damage to the eye’s nerves and irreversible blindness in the form of visual field loss.
- Vitreous Hemorrhage:
A newly developed blood vessel begins to leak into the vitreous gel filling the eye preventing light from entering the retina. In mild cases, symptoms include floaters, i.e., seeing shapes like a spider web, mosquito, dots, lines etc. In severe bleeding, there is a sudden profound loss of vision. Visual recovery, in this case, is complete if the retina is not damaged by diabetic retinopathy.
- Detached Retina:
Scar tissue pulls away from the retina from the back of the eye. Typically, it causes floaters, flashes of light, and severe vision loss. If left untreated, it can lead to permanent loss of vision.
Conclusion:
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any diminished or blurred vision. Taking care of diabetes and keeping it under control is the best way to protect the retina and prevent blindness due to diabetic retinopathy.
If you have had diabetes for more than five years, get your eyes tested regularly, at least once a year or as advised by your eye doctor. Control of blood pressure and monitoring of lipid profile is essential.
If you are a diabetic patient and do not have any vision problems, you should still get your eyes checked once a year.






